%%{
init: {
'theme': 'base',
'themeVariables': {
'fontSize': '30px'
}
}
}%%
flowchart LR
climate(Climate) --> vector(Disease vectors) --> health(Human health)
climate --> health
climate --> social(Social & economic \n determinants) --> health
Disease and climate data fusion for modelling
An application case for Brazil
Raphael Saldanha
Inria, GHR collaborator
2023-11-22
Introduction
- Postdoc researcher at Inria, a French research institute for digital science and technology
- BSC, Global Health Resilience collaborator
- Fiocruz, Climate and Health Observatory
Climate sensitive diseases
Direct relationship: floods, droughts, heat waves…
Indirect relationship
- Climate necessary conditions to vector viability, reproduction and disease transmission efficiency
- Climate indicators may act as proxy variables to vector distribution on statistical models
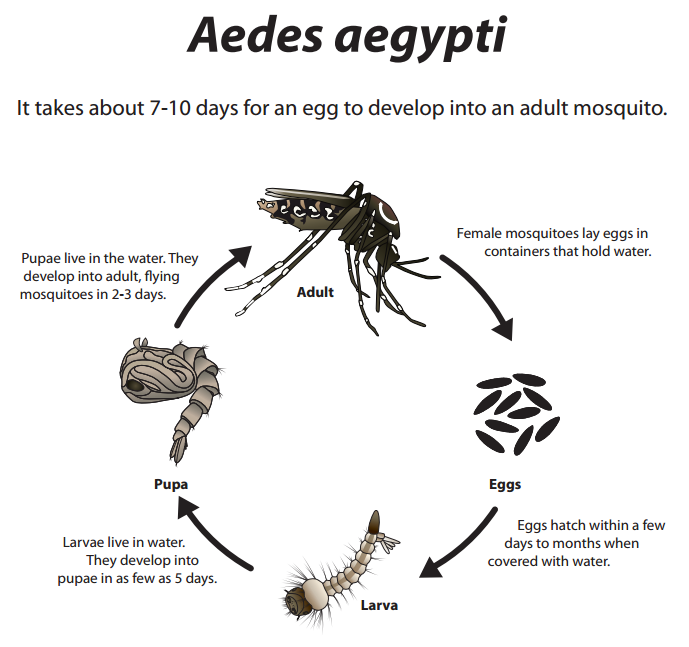
A time-lagged relationship
- Vector life cycle in a time perspective
- Climate conditions from the past leads to the disease incidence of today
Climate data
- Data sources
- Weather stations, rain gauges
- Satellites
- Data products
- Statistical surface interpolations
- Model reanalysis
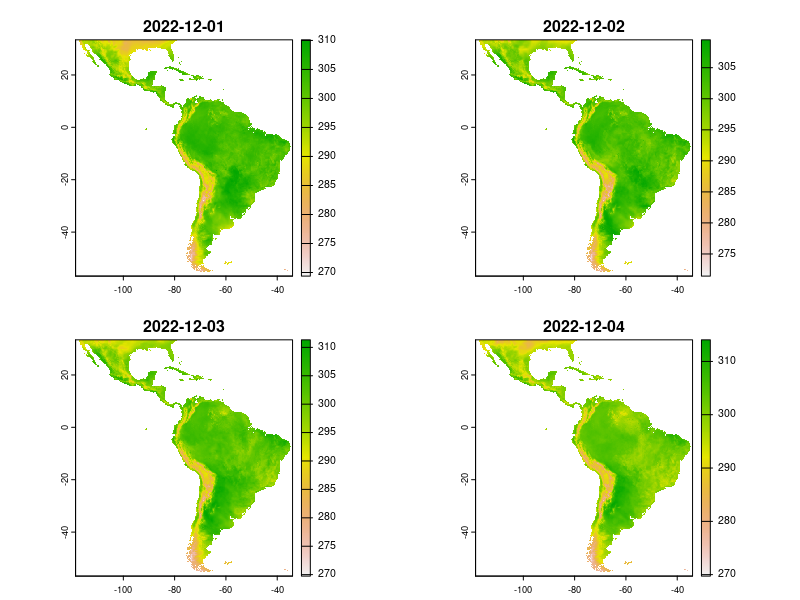
ERA5-Land reanalysis
- Copernicus, ECMWF
- Global coverage
- Hourly data
- 1950 to the present (one week lag)
- Spatial resolution ~9km
- Several climate indicators
Data structures
- Climate indicators: grid data
- Disease incidence: tabular, individual cases aggregated by spatial regions and time spans

Fusioning data
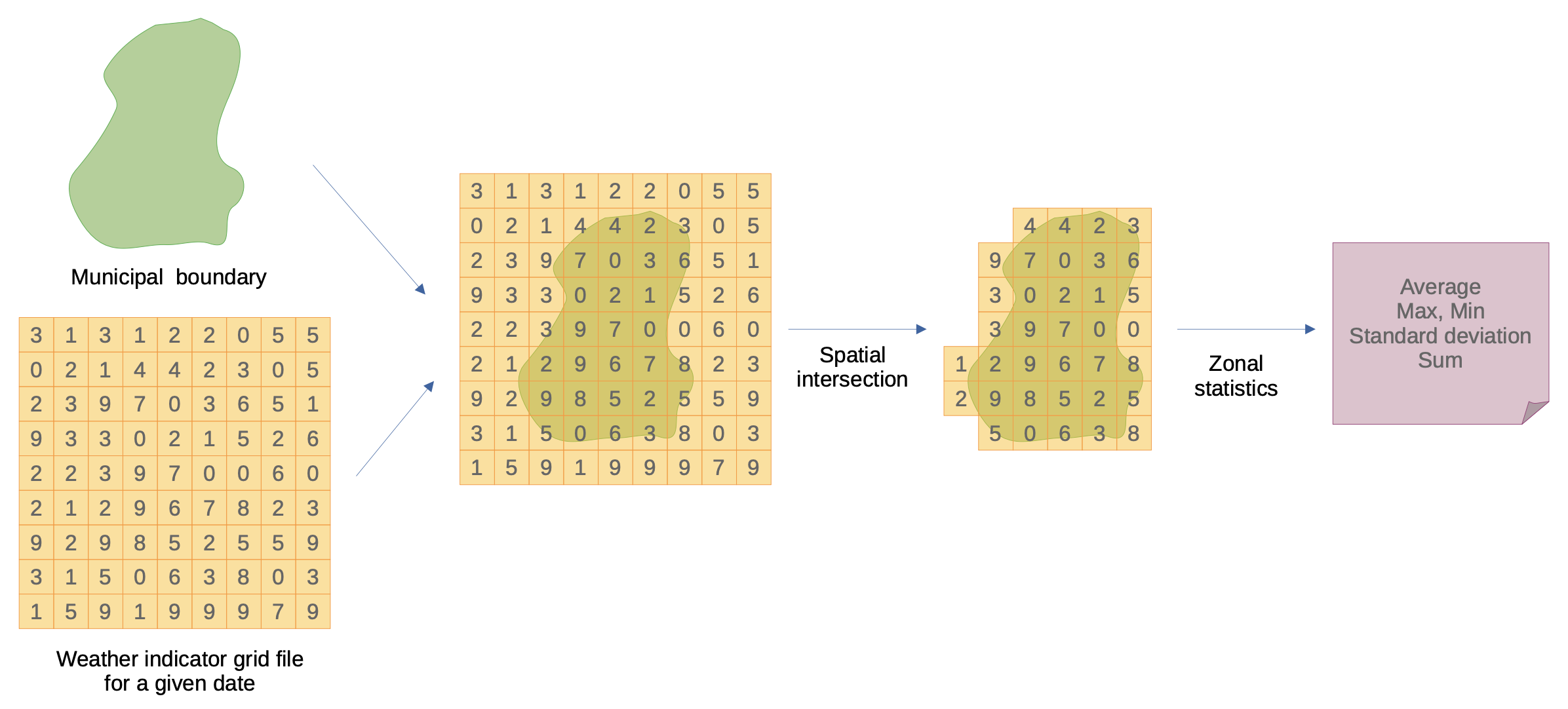
Case example
Zonal Statistics of Climate Indicators from ERA5-Land for Brazilian Municipalities, 1950-2022
- ERA5-Land hourly data to daily aggregates
- Average, maximum and minimum temperature, total precipitation
- Surface pressure, dewpoint, \(u\) and \(v\) components of wind
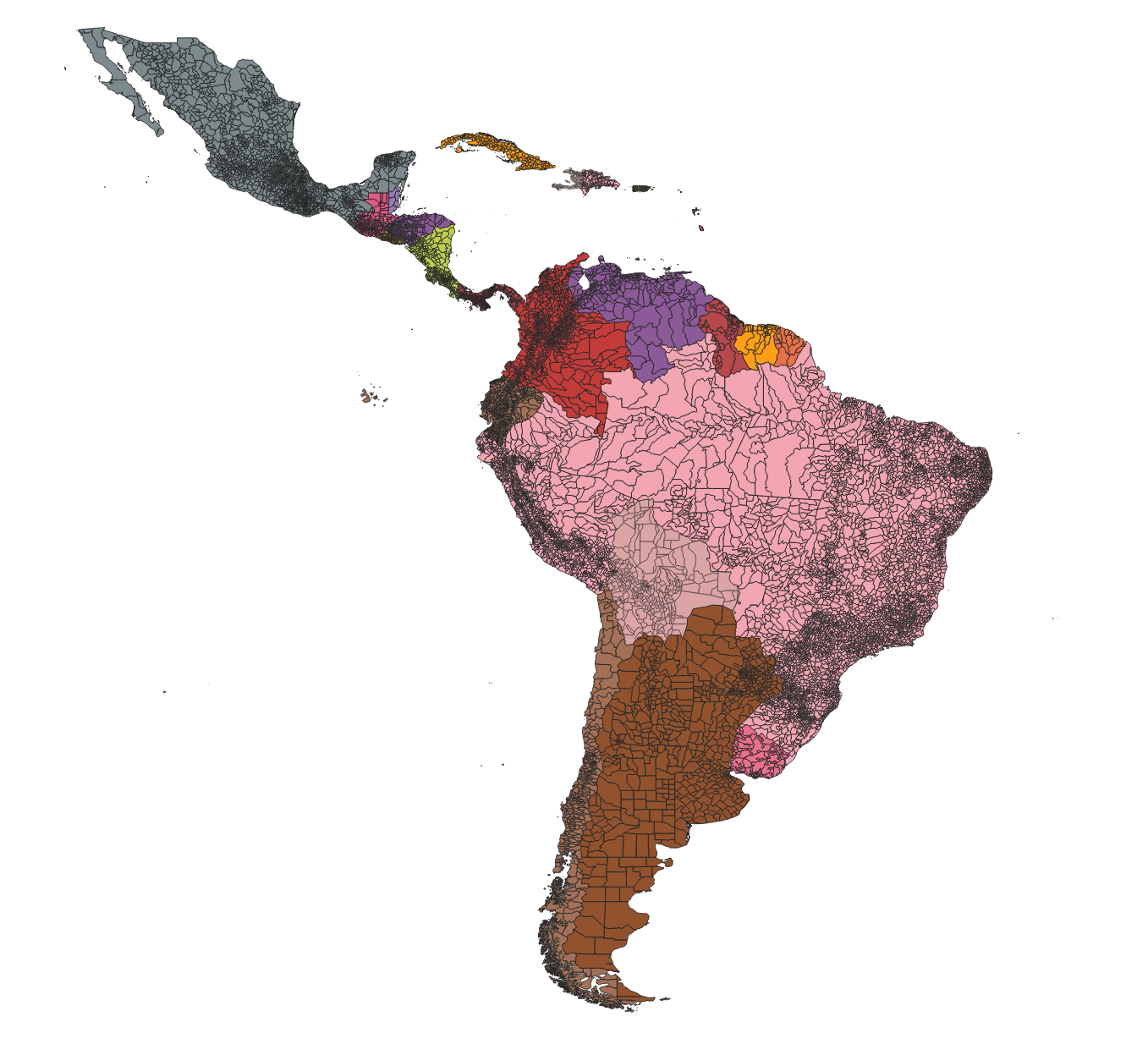
- Zonal statistics computation for the 5,570 Brazilian municipalities
- Minimum, maximum, average, sum, standard deviation, cell count
Workflow
%%{
init: {
'theme': 'base',
'themeVariables': {
'fontSize': '30px'
}
}
}%%
flowchart TD
era5(ERA5-Land \n indicators) --> hdata(Hourly data)
bb(Latin America \n bounding box) --> hdata
hdata --> agg(Daily aggregated \n data)
agg --> mun(Municipal boundaries)
mun --> zs(Zonal statistics)
Results
| ERA5-Land indicators | Daily time-aggregating functions | Spatial zonal statistics |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (2m) | mean, max, min | max, min, stdev, count |
| Dewpoint temp. (2m) | mean | max, min, stdev, count |
| \(u\) component of wind | mean | max, min, stdev, count |
| \(v\) component of wind | mean | max, min, stdev, count |
| Surface pressure | mean | max, min, stdev, count |
| Total precipitation | sum | max, min, stdev, count, sum |
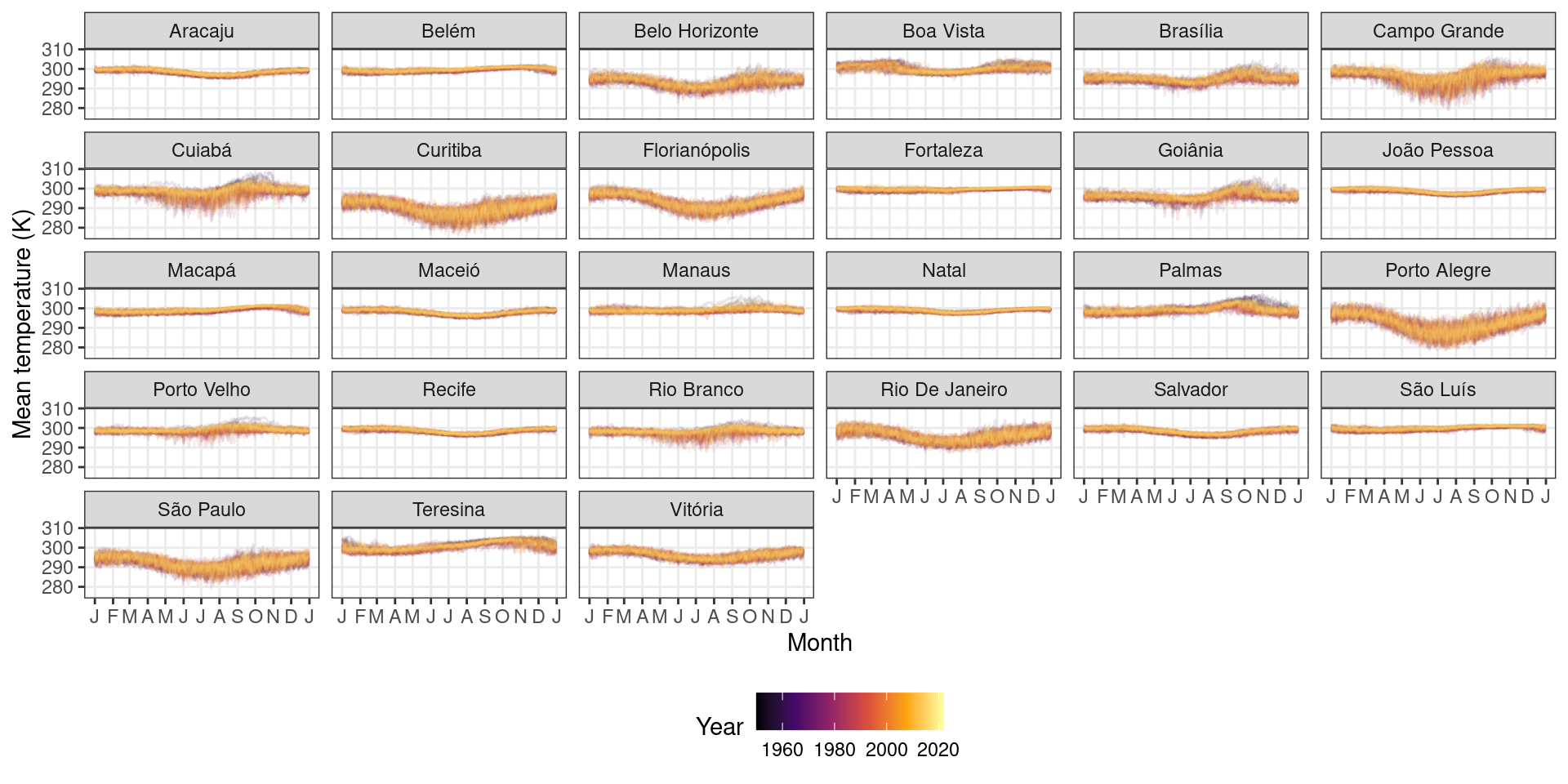
Average temperature
Next steps…
- Continuous update
- Human settlements, population-weighted zonal statistics
- Compute climate time-series features: heat waves, persistent rains, etc.
- Expand methodology to other countries
Thanks!
Contact, data links, R packages and short tutorials available at rfsaldanha.github.io
